The latest enhancements of numerical weather prediction models are leading to better forecasting skill, more localised predictions and longer forecasting periods.
The atmospheric research facility in Cabauw aims to acquire knowledge on observations and to innovate meteorological observation techniques and products that are essential for the operational services and atmospheric research of KNMI.
GeoWeb is an web-based integrated system that is currently being developed at KNMI to realize the next generation tooling for monitoring the atmosphere by forecasters, scientists and developpers.
Accurate quantitative precipitation estimates are important for a wide range of applications. Therefore KNMI is working on enhancing the quality of its radar- and rain gauge-based precipitation products.
We will create an unprecedented three-dimensional picture of the great “skies over Holland”, pioneered in canvas and paint by the famous 17th-century artist Jacob van Ruisdael.
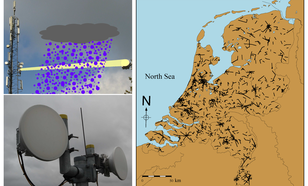
Ground-based Doppler wind lidars are laser-based remote sensing instruments that measure wind speed and wind direction up by measuring the Doppler-shift of the backscattered laser light, typically by aerosols in the moving air.
The Dutch Offshore Wind Atlas (DOWA) provides a 10 year wind climatology for the North Sea.
This service is part of the Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S). It provides climate monitoring products for Europe, based on surface in-situ observations.
The Copernicus Climate Change Service (C3S) Data Rescue Service Portal is a web-based user-updatable system to coordinate and facilitate global data rescue activities.
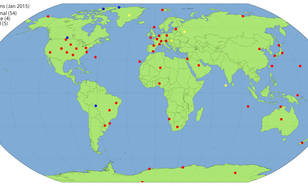
The objective of BSRN is to provide top-quality observations of the shortwave and longwave irradiances at the Earth’s surface.
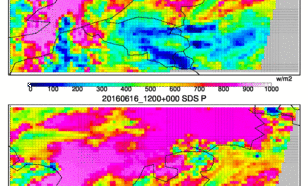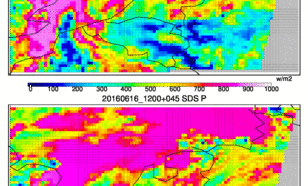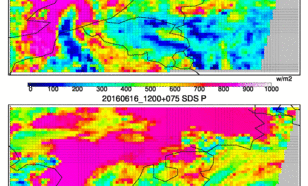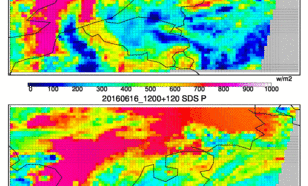
Forecasts of solar radiation are needed for the operation of solar power plants, in order to integrate stable electricity into the grid and to optimize the production of solar energy according to demand.

The European Natural Airborne Disaster Information and Coordination System for Aviation, a H2020 project. Towards closing the significant gap in European-wide data and information availability during airborne hazards.
Active member of the ESGF, a global system of federated data centers that allow access to the largest archive of climate data world-wide. Part of the European IS-ENES infrastructure.

VERCE is a data-intensive e-science environment to enable innovative data analysis and data modelling methods that fully exploit the increasing wealth of open data generated by the observational and monitoring systems of the global seismology community.
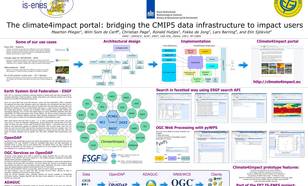
Climate4impact is a portal aiming to enhance the use of climate research data.
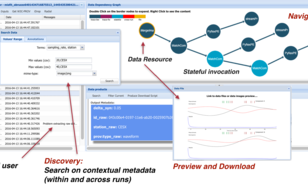
Framework for the storage and access of data-intensive streaming provenance.

KNMI Data Platform (KDP) is the access point for all meteorological, climate and seismological data in the Netherlands.

The Cabauw in-situ observational program aims at characterizing the physical aspects of the land surface and atmospheric boundary layer, and their interaction.

Continuity and quality of the meteorological surface observations are of crucial importance to end users in weather, climate and aeronautical application areas.
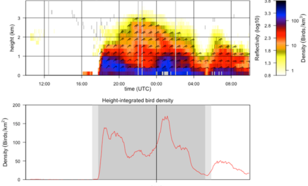
KNMI operationally monitors bird migration using its weather radars.

There are many different users of radar data (hydrologists, forecasters, ornithologists, general public, among others), and they can all benefit from polarimetry.

In the past there have always been weather enthusiasts interested in measuring weather in their direct environment.
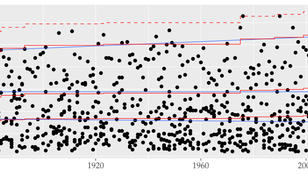
Statistical methods form the necessary scientific basis for assessing trends in climate, seismicity, and the likelihood of extreme events and associated hazards.