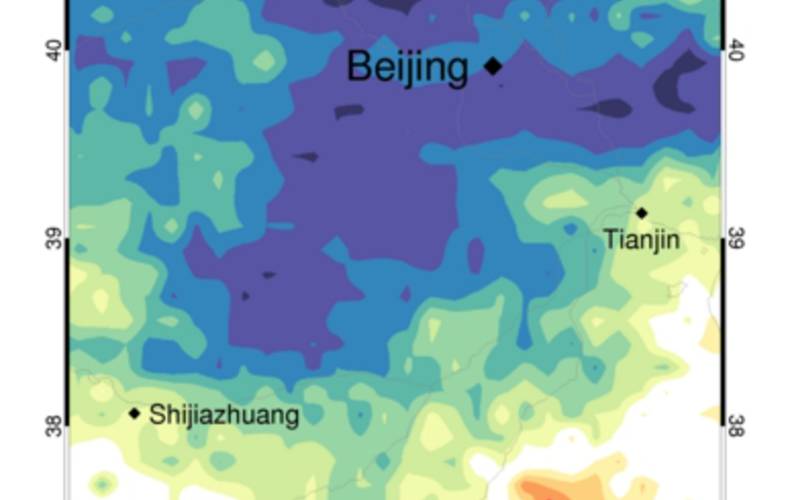
During the 2008 Olympic and Paralympic Games in Beijing (from 8 August to 17 September), local authorities enforced strong measures to reduce air pollution during the events. To evaluate the direct effect of these measures, we use the tropospheric NO2 column observations from the satellite instruments GOME-2 and OMI. We interpret these data against simulations from the regional chemistry transport model CHIMERE, based on a 2006 emission inventory, and find a reduction of NO2 concentrations of approximately 60% above Beijing during the Olympic period. The air quality measures were especially effective in the Beijing area, but also noticeable in surrounding cities of Tianjin (30% reduction) and Shijiazhuang (20% reduction).
B Mijling, RJ van der A, KF Boersma, M Van Roozendael, I De Smedt, HM Kelder. Reduction of NO2 detected from space during the 2008 Beijing Olympic Games
Status: published, Journal: Geophys. Res. Lett., Volume: 36, Year: 2009, doi: 10.1029/2009GL038943